If you ask what is energy? some people will tell you that energy is an abstract thing. This was how Richard Feynman described it in the Feynman lectures, volume I chapter 4. He used the analogy of children’s blocks. He said these blocks were absolutely indestructible and could not be divided. But then he said there are no blocks. Only then he contradicted himself by saying energy has a number of different forms, such as gravitational energy, kinetic energy, and heat energy:
 Image from Assignment point
Image from Assignment point
Then for the cherry on top he said this: “It is important to realize that in physics today, we have no knowledge of what energy is”. Only it isn’t true. Einstein knew what energy was. Now I’ve always been a Feynman fan, and an Einstein fan too. But as I’ve learned more about the physics and the history, I’ve come to appreciate that Feynman was something of a young Turk who did his own thing. One of his close colleagues was Freeman Dyson. In 2007 Dyson told me that way back in the late forties, people like him considered Einstein to be out of touch. So I don’t think Feynman read Einstein’s material. That’s why he didn’t know how gravity works. Or that curved spacetime is not the same thing as curved space. Or that energy is not an abstract thing.
Energy is not just the capacity to do work
Nor is it just the capacity to do work. That’s the answer you usually get: energy is the capacity to do work. But when you then ask what is work? The answer is merely the transfer of energy. That’s circular, and a non-answer pretending to be an answer. That’s unsatisfactory. See for example what Cathal O’Connell said in Cosmos magazine: “Any physics textbook will tell you energy is ‘the capacity to do work’. Then it usually goes on to explain that ‘work’ is the action of moving something against a force. But isn’t this definition kind of unsatisfying?” Yes it is. Energy is not just the capacity to do work, so well said that man. Unfortunately he then said this: “the reason energy is so hard to define is because it’s an abstract notion. In physics, the concept of ‘energy’ is really just a kind of shorthand, a tool to help balance the books”. There’s that energy is an abstract thing again. He also said there is no physical essence of energy, and no such thing as pure energy, and that energy is always carried by something. Only then he contradicted himself by saying energy can be converted into mass. Try pushing a car and you will soon appreciate that mass is not an abstract thing.
Energy is not just the property of a thing
If energy can be converted into mass, and mass is not an abstract thing, that means energy is not an abstract thing either. So it isn’t just some property of a thing. It isn’t like “red”. I can show you a red balloon, a red bus, or a red red ruby. But I can’t remove this red and hold it in the palm of my hand. I can remove the paint or the dye, and I can hold that in the palm of my hand. But I’m still holding a thing that is red. You always need a thing to be red. There is no such thing as pure red. It isn’t like that for energy. If it was, energy couldn’t be converted into mass, and it can. This is why “the mass of a body is a measure of its energy content”. That’s what Einstein said in his 1905 E=mc² paper, and he meant what he said. His paper was entitled does the inertia of a body depend upon its energy-content? and the answer is yes. He used an L for Lagrangian instead of an E for energy, but that doesn’t matter. What matters is that he referred to electron and body on the same line, and he said this: “If a body gives off the energy L in the form of radiation, its mass diminishes by L/c²”. That means when you burn wood in a fire, the total mass of the ash and smoke and gas is less than the original mass of the wood. That’s because a burning log is a body that gives off energy in the form of radiation. Note that according to Einstein, radiation doesn’t have energy, it’s a form of energy. That’s important. Also note that according to Einstein, a body contains energy. According to Einstein, energy is something real, not just some abstract thing, and not just the property of a thing. Let’s play the detective and look into it further.
Biochemical energy
How do you make that car move? You push it. You put your back into it. You use your muscles. You do work on it. You give it kinetic energy. You add energy to it. How does this work? Via ATP and myosin. See what the Utah Learn Genetics website says: “Adding a third phosphate group (phosphorylation) adds energy, like compressing a spring. Removing the phosphate group (hydrolysis) releases energy, like freeing a spring to uncoil.
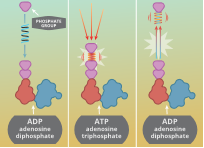 Image from the Utah Learn Genetics website
Image from the Utah Learn Genetics website
Your muscles employ what can only be described as molecular springs. The atoms in those molecules are held together by bonds, and these bonds rely on electrons and the electromagnetic force. They’re rather like magnets that want to pull together or push apart, only it’s electrostatic attraction and repulsion rather than the magnetic variety. Push two magnets together and hold them there, and you’re storing energy. It’s similar when you compress a coil spring. It’s similar for the energy stored in ATP. In all cases the energy is real. That’s why you can use it to push a car.
Chemical energy
It’s the same for chemical energy. See the Wikipedia article on gasoline and note that there’s a section entitled energy content. Gasoline, also known as petrol, contains energy. When you drive your car, petrol is burnt in the engine. That’s like releasing a zillion molecular springs all at once. The petrol and oxygen turn into a hot expanding gas mixture in the cylinders. This pushes the pistons which turn the crankshaft, which turns the propshaft, which turns the wheels. The Wikipedia article says one component of petrol is octane, the combustion of which involves this chemical reaction:
2 C₈H₁₈ + 25 O₂ → 16 CO₂ + 18 H₂O
In essence the octane is behaving like an uncoiling spring, albeit one which is uncoiled using oxygen, and where the component parts are then rerarranged. It’s similar for an explosive. See what Philip Eaton et al said in their 2002 paper Octanitrocubane: A New Nitrocarbon: ”The large bond angle deformations in cubane make it a powerhouse of stored energy. Each strained bond is like the spring in a set mousetrap”. Cubane is strained. It’s under stress. Each strained bond is like the spring in a set mousetrap. When this explosive detonates it’s like releasing a zillion molecular springs all at once. The result is an explosion of devastating force.
Nuclear energy
It’s similar with nuclear energy, only now we’re talking about the stuff inside the atoms rather than between the atoms, and these springs are stronger. That’s why nuclear bombs are more devastating than high explosive bombs. The most powerful nuclear bomb detonated to date was the Tsar Bomba. It was an H-bomb which weighed about 30 tons and yielded about 50 megatons. However the yield was reduced from a possible 100 megatons to save the aircraft that dropped the bomb, so we’re talking about a power-to-weight ratio that’s circa three million times that of conventional explosives. The mushroom cloud was forty miles high:
 Fair use image from the Russian department of Atomic Energy Minatom), see Wikipedia and web.archive.org
Fair use image from the Russian department of Atomic Energy Minatom), see Wikipedia and web.archive.org
Interestingly however the E=mc² matter-to-energy conversion rate was remarkably low. See what “Eli” said on physics stack exchange. Only about 327 kg of hydrogen took part in the proton-proton fusion reaction with the H-bomb. This has an efficiency of 0.712%. So only 2.33 kg of matter was converted into energy. That’s about the same as the bag of potatoes in your shopping trolley.
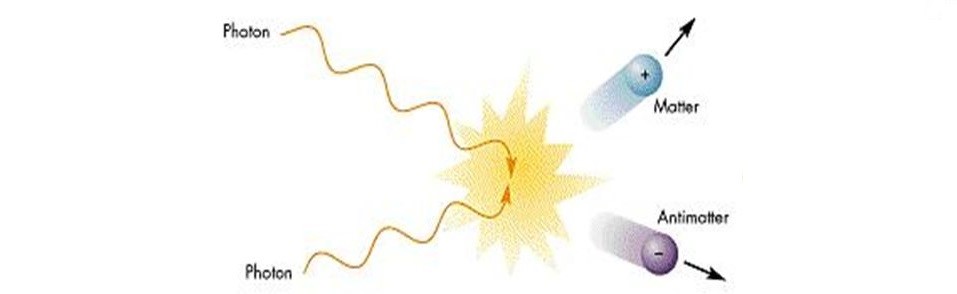
Matter-antimatter annihilation
The efficiency of hydrogen fusion pales into insignificance when compared with matter-antimatter annihilation. When we annihilate an electron with a positron, the matter-to-energy conversion rate is 100%.
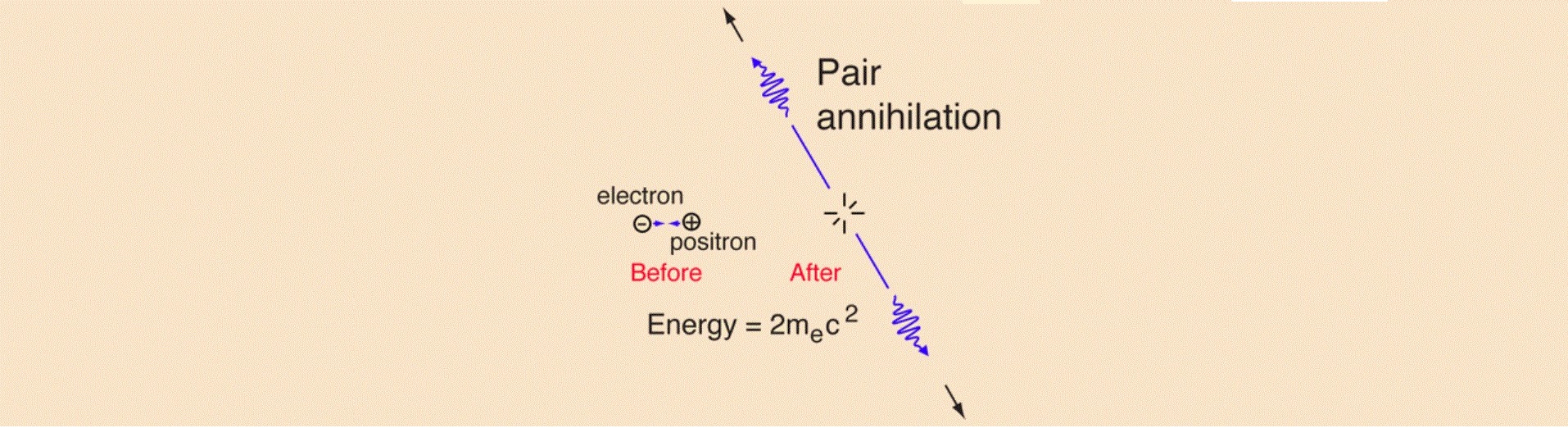 Image from Rod Nave’s hyperphysics
Image from Rod Nave’s hyperphysics
If a combined mass of 2.33 kg of matter and antimatter were to annihilate, the result would be a mushroom cloud forty miles high. Everything within a blast radius of forty miles would be totally destroyed. Windows would break five hundred miles away. There’s an awful lot of energy tied up as matter.
Gravitational potential energy
I think that demonstrates how gentle things are in ordinary life. When you compress a spring you do work on it. You add energy to it, so by virtue of E=mc² you increase its mass. The increase is so slight as to be unmeasurable, but nevertheless there is an increase. It’s similar when you lift a brick. You do work on it. You add energy to it, so by virtue of E=mc² you increase its mass. The opposite occurs when you drop a brick. Then gravity converts potential energy into kinetic energy. When the brick hits the ground the kinetic energy is dissipated, and you’re left with a mass deficit. See the Wikipedia binding energy article. Don’t think the potential energy is in the gravitational field or in “the system”, it’s in the brick. When you know how gravity works, you know this. You also know that there is no magical mysterious mechanism by which that kinetic energy somehow streams into the brick as it falls. It was always in the brick, as potential energy, which was mass-energy. You also know that gravity merely converts internal kinetic energy into external kinetic energy. Why? It’s because mass-energy is kinetic energy. You can work this out from Compton scattering and pair production.
Compton scattering
In Compton scattering some of the photon kinetic energy is converted into electron kinetic energy. The photon changes direction so it’s decelerated in the vector sense, and its wavelength increases. The electron is deflected in a direction opposite to the photon, and is accelerated in the usual sense:
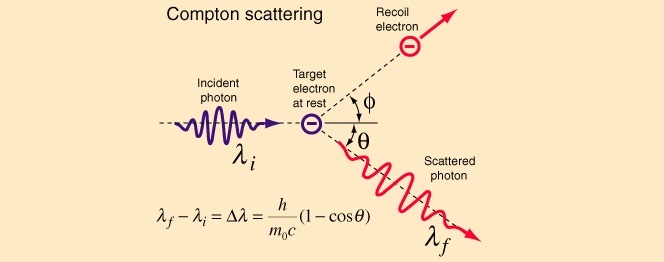 Image from Rod Nave’s hyperphysics
Image from Rod Nave’s hyperphysics
The point to note is this: if you could do another Compton scatter on this self-same photon, and another and another ad infinitum, in the limit there’s no photon left. That’s because the photon is a singleton soliton electromagnetic wave in space, and it has an E=hf or E=hc/λ wave nature. A wave in the surf has a wave nature too. Note that when you take all the kinetic energy away from a wave in the surf, it just isn’t there any more. So the wave in the surf is energy. It’s the same for a photon. When you take all the kinetic energy away from a wave in space, it just isn’t there any more. So the photon is energy. Perform Compton scattering repeatedly with the self-same photon, and in the end it has been entirely converted into the kinetic energy of electrons.
Pair production
And yet, and yet: in pair production, you can make an electron and a positron out of photons. So the electron is kinetic energy too. But now this kinetic energy is hidden. We call it mass-energy. Or potential energy. Or field energy. Only there’s angular momentum in this field, and a secret Poynting vector going around and around. See page 26 of Schrödinger’s quantization as a problem of proper values, part II. That’s where he said “let us think of a wave group of the nature described above, which in some way gets into a small closed ‘path’, whose dimensions are of the order of the wave length”. Also see Hans Ohanian’s 1984 paper what is spin? He said “the means for filling the gap have been at hand since 1939, when Belinfante established that the spin could be regarded as due to a circulating flow of energy”. Frederik Belinfante’s paper was on the spin angular momentum of mesons. This circulating flow of energy is why electrons have their dipole magnetic moment, and go round in circles or helixes in a uniform magnetic field. That’s why the electron is a “spinor”. And this circulating flow of energy is there because in gamma-gamma pair production, the photon paths change from a straight linear paths, to closed paths:
 Pair production image accredited to McGraw Hill Higher Education, see Google
Pair production image accredited to McGraw Hill Higher Education, see Google
The opposite happens when you annihilate that electron with a positron. That’s why you see 511 keV photons racing away at the speed of light. From what looked like a standing start, but wasn’t. That’s because in atomic orbitals and everywhere else, electrons exist as standing waves.
Electrons are standing waves
Take a look at the enigmatic electron by Frank Wilczek. He said “the proper quantum mechanical description of electrons involves wave functions, whose oscillation patterns are standing waves”. Standing waves that only look like they’re motionless. Standing waves that are energy, a circulating flow of energy in the guise of a “body” called an electron. A body that doesn’t have a field, it is field. Standing wave, standing field. It isn’t some billiard-ball thing that has charge, it is charge, because it’s a 511keV field-variation wave wrapped and trapped in a twisting turning spin ½ Möbius loop that makes the field variation look like an all-round standing field. The positron is similar, but with the opposite chirality. It has the same mass, because as hinted at by the wave nature of matter and electron spin, mass is just resistance to change-in-motion for a wave going round and round. Annihilation is like unwrapping one standing wave with another, and then both waves aren’t standing any more. Instead they’re off like a shot. It’s similar in low-energy proton-antiproton annihilation. What you see is gamma photons. Energy in the form of radiation:
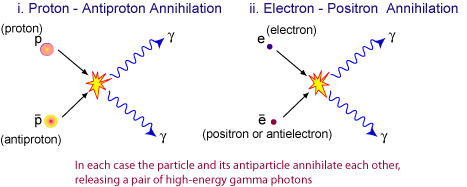 Image credit: CSIRO Australia Telescope National Facility
Image credit: CSIRO Australia Telescope National Facility
Remember what Einstein said: if a body gives off the energy in the form of radiation, its mass diminishes. Only when annihilation occurs, two bodies give off all their energy in the form of radiation and their mass diminishes to zero. The bodies lose all of their mass, and then they’re just not there any more. Because the electron is just a self-trapped 511keV photon in a chiral spin ½ configuration, and so is the positron. Which tells you what happens in Compton scattering: a portion of the photon gets shaved off and applied to the electron. So now the standing wave electron isn’t symmetrical any more. The wave still goes around and around, only it doesn’t end up where it started. As a result the electron moves.
Electron orbitals
Something similar happens inside the atom. When a hydrogen atom absorbs a low-energy photon, the electron moves, But it’s bound to the proton, so it doesn’t move totally away. Instead it changes orbital. It’s something like a tetherball, only it’s more like a tethered hoop of light. Only it isn’t some thin hoop, it’s a fat torus, so fat that it looks spherical. Only when it changes orbital, it can look different. It can look like a torus, or a dumbbell, or a mixture of both:
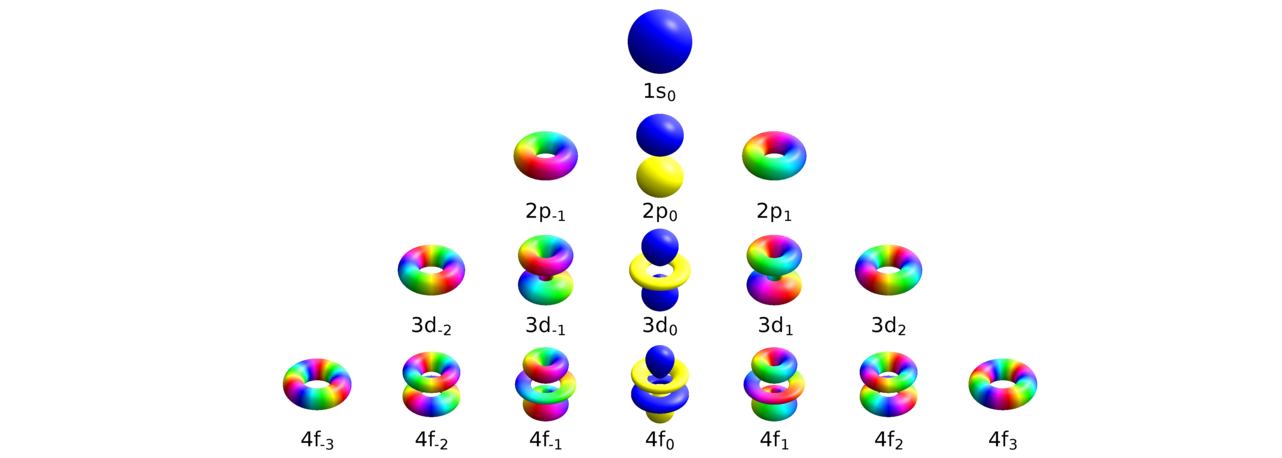 CCASA image by Geek3, see Wikipedia
CCASA image by Geek3, see Wikipedia
Note that these electron orbitals don’t really have a surface, just as a magnetic field doesn’t have a surface. Also note that these electron orbitals can get more complicated and form bonds. Like I was saying, close your eyes whilst you play repulsion with a couple of magnets, and you can feel the field. The electron is like that field, minus the magnets. Push two magnets towards one another, and it feels like a spring. It would be similar if you could push two electrons together. You are storing energy. Only spring steel springs are made of things like electrons and protons, which are themselves made of energy. So when you store energy in a spring, you are storing energy in energy, because matter really is made of energy. You are too, along with all the matter you can see, and all the light you can see with.
The photon is just a wave in space
Light is energy because it has a wave nature. It’s comprised of photons, but don’t think of the photon as some billiard-ball particle. Wave-particle duality is a myth. Particles are waves. The photon has a wave nature. See Pascual Jordan’s resolution of the conundrum of the wave-particle duality of light by Anthony Duncan and Michel Janssen dating from 2007. On page 47 they quote Jordan saying this: “The fluctuation effects, which prove the presence of corpuscular light quanta in the radiation field, then arise automatically as consequences of the wave theory. The old and famous problem [of] how one can understand waves and particles in radiation in a unified manner can thus in principle be considered as solved”. As for what sort of wave the photon is, see what Maxwell said when he was talking about displacement current in 1861: “light consists of transverse undulations in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena”. Also see what Percy Hammond said in the 1999 Compumag: “We conclude that the field describes the curvature that characterizes the electromagnetic interaction. Then think about some other waves. When an ocean wave moves through the sea, the sea waves. When a seismic wave moves through the ground, the ground waves. So, what waves when a light wave moves through space? There can only be one answer, and that answer must be space. Space waves. A photon is just a wave in space. Don’t think of it as an electric wave and an orthogonal magnetic wave. It’s an electromagnetic wave. Or better still, it’s a wave of electromagnetic four-potential. Think of it as a pressure-pulse of space propagating through space.
Spatial energy
But don’t think all energy takes the form of light and matter. Yes, you can think of a 511keV photon as a wave in space moving linearly at c, and you can think of an electron as the same thing trapped in its own spatial curvature. But dark matter doesn’t consist of photons and electrons. Nor does gravitational field energy. Einstein said “the energy of the gravitational field shall act gravitatively in the same way as any other kind of energy”. But it isn’t made of particles. It’s spatial energy. Don’t forget that some say the cosmological constant is the “energy density of the vacuum of space”. Or that the modern approach is to treat dark energy as a component of the stress-energy-momentum tensor which “describes the density and flux of energy and momentum in spacetime”:
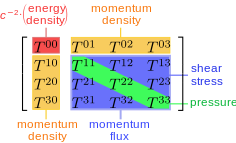 Public domain image by Maschen, based on an image by Bamse see Wikipedia
Public domain image by Maschen, based on an image by Bamse see Wikipedia
The shear stress term on the right tells you we’re dealing with some kind of elastic continuum. The energy-pressure diagonal tells you it’s subject to pressure. For an analogy, imagine you have a block of gin-clear ghostly elastic jelly, with grid lines in. You slide a hypodermic needle into the centre of the block, and inject more jelly. This represents a concentration of energy bound up as the matter of a massive star. It creates a pressure gradient in the surrounding jelly. That might sound novel, but it isn’t. Even Newton knew about this. Léon Rosenfeld talked about it 1969:
 Fair use excerpt from Newton’s views on aether and gravitation by Léon Rosenfeld 1969
Fair use excerpt from Newton’s views on aether and gravitation by Léon Rosenfeld 1969
Stress is directional pressure, the pressure is outwards, and Einstein’s equation Gμν = 8πTμν is modelling the way gin-clear ghostly elastic space is conditioned by the energy you added. But don’t forget that you added jelly to represent energy, and that the jelly also represents space. Space doesn’t just have some kind of innate intrinsic vacuum energy. At some deep fundamental level, space and energy are two sides of the same coin.
Space is aether
Did you notice the reference to aether in Rosenfeld’s paper? Einstein is said to have done away with the aether, but he didn’t. His 1920 Leyden address was on ether and the theory of relativity. He said “according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an ether”. Also see Gustav Mie’s 1913 Foundations of a theory of matter translated by David Delphenich. In chapter 1 section 4, Mie talked about “the so-called ‘four-potential’ that one constructs from the scalar potential j and the vector potential f.” He said “the two potentials, j and f, embody the physical state of the universal ether”. In addition take a look at the Wikipedia aether theories article where you can read Robert Laughlin saying most physicists think space is more like a piece of window glass than ideal Newtonian emptiness.
The contrast between space and matter would fade away
This is important, because in his Leyden Address, Einstein said if we could understand the gravitational and electromagnetic fields “as one unified conformation”, the contrast between ether and matter would fade away. He was saying the contrast between space and matter would fade away. See does matter differ from vacuum? by Christoph Schiller. The answer is no. See Helge Kragh’s preludes to dark energy. He tells how Einstein delivered a lecture in Nottingham in 1930 saying space “remains the sole medium of reality”. What’s a gravitation field? A pressure gradient in space. Why does the universe expand? Because space has an innate pressure. What’s a photon? A pressure-pulse of space propagating through space. It has a polarization, so the pressure is directional, so we call it stress. It doesn’t matter whether you call it pressure or stress, because either way, matter is made from it. That’s why in 1870 William Kingdon Clifford came up with his space theory of matter on Wikipedia.
Energy is a volume of stressed space
There’s nothing more fundamental than space. Space isn’t made of anything else. We can’t examine atoms of space through a microscope or annihilate it to obtain something else. But we know that the dimensionality of energy can be expressed as pressure x volume, and that space always has a volume. If it didn’t, it wouldn’t be space. We also know that space is always stressed, because gravitational fields are everywhere, as is light, and because space expands. So we know that in barest essence, at the deep fundamental level, energy is a volume of stressed space. The greater the volume, the more energy there is. The greater the stress, the more energy there is. Energy isn’t just earth, air, fire, or water. It isn’t just some classical element: “Aristotle added a fifth element, aether; it has been called akasha in India and quintessence in Europe”. Aether is space and space is energy. It’s the quintessence. But in truth it’s the first essence, and the only essence. Because it’s the only thing. The one thing we can neither create nor destroy. The thing from which all other things are made.
Wilzek paper on electron link is broken.
Thanks Harald. I fixed it. The paper was published as The enigmatic electron. I have inserted not one but two links to it. I’ve done the same fix in my electron article. I do wish all papers were freely available. Joe public pays billions to fund science, then has to pay though the nose to see the results. Nature want $8.99, the price of a book, for a two-page paper.
Hello again John.
Do you know about the Synergetic theory by Rene-Louis Vallee?
http://jnaudin.free.fr/vsg/synergetics.pdf
I read about it more than 10 years ago, and it sounds very similar to the pair production and anihilation stuff you talk about.
There’s even some devices trying to get advantage of K-electron capture using E and B fields:
http://jnaudin.free.fr/vsg/protelf.htm
All the information about these devices (VSGs) is here:
http://jnaudin.free.fr/vsg/index.htm
It doesn’t ring a bell. I just took a look. No, I don’t think I’ve seen this before. Some of it sounds wrong, like the photon picture on page 34, and I don’t like the way he talks of electric fields and magnetic fields. But some it sounds promising. Like this on page 46: “The electron, the proton and undoubtedly the neutron must thus be presented as electromagnetic systems of waves stationed with high density of energy, which are reflected inside one or several microscopic disruptive surfaces”.. I’m not so keen on the PROTELF though. And in your last link he gets gravity wrong and talks about a multitude of ultra high frequency waves being propagated in all directions.
“At some deep fundamental level, space and energy are two sides of the same coin.” – I agree with this.
.
“energy is a volume of stressed space. The greater the volume, the more energy there is. The greater the stress, the more energy there is” – I’m not so sure about this. Reading your great posts the past few days John I’ve been coming to a slightly different conclusion, that energy is negative space, or put another way that space is negative energy. By negative space I mean non-space, the opposite of space. A hole in space is energy. Photons, particles, black-holes, they are all holes in space, inaccessible regions, voids. The holes create the stressed volume of space. The electromagnetic wave is the effect of a hole travelling through space, as you say it is something like the curviness of space, but at the heart of the photon is a hole in space.
.
Going back to your gin-clear ghostly elastic jelly and the hypodermic needle, the needle doesn’t
inject more jelly to create energy, it injects a bubble (a void), (or possibly equivalently, instead of injecting, another way of looking at it is it sucks out a region of space such that the jelly around the point is pinched in)
.
Why do photons of different wavelengths have the same amplitude? We can’t answer that question if we’ve got the wrong idea of a photon, the wave of a photon is the effect the bubble has on the surrounding space as it moves through it. When the bubble is moving in a certain direction at the speed of light, due to length contraction, it is not spherical but compressed into a cut. If you are sitting on an electron watching photons zip by, you don’t see bubbles of various sizes wizzing by, you don’t see a bubble at all, because it has zero width, but you can detect the effect it has on space where you are, the effect is an electromagnetic wave. If you were to look at this scene from an absolute perspective you would notice that a large bubble results in the same wavelength wave as a small bubble, i.e. the wavelength doesn’t vary but the size of the bubble (amplitude) does. But you are sitting on the electron looking locally not absolutely, and looking locally you see constant amplitude waves of varying wavelengths. Phrased slightly differently: constant amplitude waves of varying wavelength are kind of the same a varying amplitude waves of constant wavelength.
Very much like how from the absolute perspective the speed of light is spatially variable, but if you measure it anywhere you get the same answer.
.
With this idea, it’s easy to see why/how one can split a short wavelength photon into two longer wavelength photons, it’s just splitting a bubble in two.
.
Also easy to see that a black hole is formed when you get so many little bubble in one area that all those little bubbles merge into one huge bubble.
.
This thinking, that energy is negative space, leads to the fairly natural conjecture that [total space in the universe] + [total energy in the universe] = zero. Which, googling around appears to be something Hawking concluded also.
.
These are my current thoughts anyway, probably all wrong, what do you reckon? Thanks for the great articles!
What do I reckon? I don’t think there’s a lot wrong with your bubble concept provided it’s a bubble of air in air. Like I said in my other comment, your bubble exerts an outward pressure on the gin-clear ghostly elastic jelly because it’s comprised of air under pressure. There’s not a huge difference between air and gin-clear ghostly elastic jelly. Air is a gin-clear fluid and it isn’t ghostly, but that doesn’t matter if we’re only talking about bubbles of the stuff. If energy was non-space, then if you carved out a spherical hole in space then retreated to a safe distance, the pressure in the surrounding space would make the hole collapse inwards.
.
Why do photons of different wavelengths have the same amplitude? We can’t answer that question if we’ve got the wrong idea of a photon, the wave of a photon is the effect the bubble has on the surrounding space as it moves through it. When the bubble is moving in a certain direction at the speed of light, due to length contraction
.
The important thing about this is that photons do not suffer length contraction. Radio-wave photons have a wavelength measured in kilometres. Whilst I consider myself a relativity guy through and through, I don’t like what people say about length contraction. If you and I are both lying prone in our spacesuits and are measured at 2m long, then if I accelerate towards you and pass you by very fast, I might measure you as being 1m long. I measure you as length contracted, but you haven’t changed at all. Instead I have. Think about it.
.
If you are sitting on an electron watching photons zip by, you don’t see bubbles of various sizes wizzing by, you don’t see a bubble at all, because it has zero width, but you can detect the effect it has on space where you are, the effect is an electromagnetic wave. If you were to look at this scene from an absolute perspective you would notice that a large bubble results in the same wavelength wave as a small bubble, i.e. the wavelength doesn’t vary but the size of the bubble (amplitude) does. But you are sitting on the electron looking locally not absolutely, and looking locally you see constant amplitude waves of varying wavelengths. Phrased slightly differently: constant amplitude waves of varying wavelength are kind of the same a varying amplitude waves of constant wavelength. Very much like how from the absolute perspective the speed of light is spatially variable, but if you measure it anywhere you get the same answer.
.
I’m sorry, I don’t like this. I prefer an analogy where space is like a lattice of guitar strings with a constant pluck amplitude. It’s easier to pluck the guitar string if it’s long, and you have to put in some real effort to pluck a short guitar string. Only the analogy is not ideal because there are no actual guitar strings, and no plectrums, just space. It’s like some gin clear ghostly elastic jelly and you can draw imaginary lines in it to visualize it, and then the only tool in the box to make those lines move apart is more space. That’s what you use to emulate the pressure of your pluck. So I think of a short-wavelength photon as a high-pressure photon.
.
With this idea, it’s easy to see why/how one can split a short wavelength photon into two longer wavelength photons, it’s just splitting a bubble in two.
.
Again, I don’t like the bubble analogy here.
.
Also easy to see that a black hole is formed when you get so many little bubble in one area that all those little bubbles merge into one huge bubble.
.
I quite like this but only because your bubble is a bubble of air under pressure, and the air isn’t a million miles away from the gin-clear ghostly elastic.
.
This thinking, that energy is negative space, leads to the fairly natural conjecture that [total space in the universe] + [total energy in the universe] = zero. Which, googling around appears to be something Hawking concluded also.
.
Jonathan, cross my heart and hope to die: the energy of the universe is colossal. I am not a fan of Hawking. If you read his papers, trust me, you won’t be either.
.
These are my current thoughts anyway, probably all wrong, what do you reckon? Thanks for the great articles!
.
My pleasure, it’s good to talk. And if we all agreed about everything, what would we talk about?
Thanks John, I appreciate your considered comments.
“your bubble exerts an outward pressure on the gin-clear ghostly elastic jelly because it’s comprised of air under pressure… if you carved out a spherical hole in space then retreated to a safe distance, the pressure in the surrounding space would make the hole collapse inwards.”
Yes, clearly the analogy breaks down if one tries to think about injecting a bubble of vacuum inside the jelly – in that case, like you say, the jelly would instantaneously fill the void and close up the bubble. But… I’m not suggesting the ‘no-space’ bubble is vacuum, rather it is anti-space, the opposite of space. In space one can move freely, but you cannot even venture into anti-space. One could say anti-space is pure 100% matter, or pure 100% energy. Or that space is the true anti-matter.
I think to suggest that the bubble of nothingness inside the jelly is incompressible, is only as strange as saying that the vacuum of space is like an inhomogeneous jelly. I think it brings a poetic symmetry to the whole thing: what we generally think of as empty is actually unimaginably dense, what we generally think of as dense is actually complete void.
“only tool in the box to make those lines move apart is more space”,
I totally get the idea of not wanting to resort to foreign object billiard balls to describe the physics of the universe, and that there is nothing else in the toolbox apart from space. But I’m not introducing another ‘thing’ apart from space, I’m just taking the ‘nothing’ seriously. If you punch a hole in a sheet of paper with your pencil, you haven’t resorted to billiard balls.
The problem with injecting more jelly into the jelly is that, although it will distort the imaginary grid lines, it won’t create a pressure gradient, because the jelly you inserted is the same substance and will therefore take it’s fair share of the pressure. To create a genuine pressure gradient I think we need a boundary of substance. Intuitively, I think we agree, it seems abhorrent to resort to dropping a billiard ball in the jelly, but I think the incompressible bubble of nothingness is satisfactory because then the whole setup is literally “nothing more than space” 🙂
Michelangelo sculpts his David out of marble + emptiness.
But whatever, I think your blog is a work of outstanding brilliance and I’ve learnt more from reading it than from all the schooling I’ve had and books I’ve read, and I’m finding the discussion enthralling!
Thanks Jonathan. I have to go, so I’ll get back to you properly another time. But meanwhile I’d say this: computer modelling might tell you something about all this. How can you make a photon keep on going through space without dissipating? How do you arrange for all photons to have energy E=hf, such that h is common to all photons? How do you make 511keV+ photons undergo gamma-gamma pair production to yield an electron and a positron. How do you make the electron and the positron attract one another? Et cetera. I have a hunch that it will all be rather simple in the end.
Jonathan: in reply to your comment:
.
Yes, clearly the analogy breaks down if one tries to think about injecting a bubble of vacuum inside the jelly – in that case, like you say, the jelly would instantaneously fill the void and close up the bubble. But… I’m not suggesting the ‘no-space’ bubble is vacuum, rather it is anti-space, the opposite of space. In space one can move freely, but you cannot even venture into anti-space. One could say anti-space is pure 100% matter, or pure 100% energy. Or that space is the true anti-matter.
.
I’m not fond of antimatter. Have you read the mystery of the missing antimatter? I think the proton is antimatter. I view an antimatter particle as just a matter particle with the opposite chirality. To appreciate my sentiment, raise your left hand, and make a fist. Take a good look at it. That’s a fist. Now raise your right hand and make a fist. That’s an anti-fist. LOL! Anyhow, once you’ve picked up my sentiment, you’ll perhaps appreciate why I don’t have a warm feeling about anti-space. I see it the black hole interior as maybe a different “phase” of space, like ice and water. Maybe it’s something like a Bose-Einstein condensate. And maybe it can somehow turn back into space. With a bang. A big bang.
.
I think to suggest that the bubble of nothingness inside the jelly is incompressible, is only as strange as saying that the vacuum of space is like an inhomogeneous jelly. I think it brings a poetic symmetry to the whole thing: what we generally think of as empty is actually unimaginably dense, what we generally think of as dense is actually complete void. “only tool in the box to make those lines move apart is more space”
.
The thing about nothing is that I have a nasty sneaking suspicion that nothingness is what’s at the edge of the universe. That’s a place where you can’t go. Because it’s no place. There is no space beyond the edge of space. But this nothingness is different to what I think is in a black hole. It’s nothing. It isn’t space. So I imagine light rays at the edge of the universe undergo total internal reflection. Or something. I’m not sure.
.
I totally get the idea of not wanting to resort to foreign object billiard balls to describe the physics of the universe, and that there is nothing else in the toolbox apart from space. But I’m not introducing another ‘thing’ apart from space, I’m just taking the ‘nothing’ seriously. If you punch a hole in a sheet of paper with your pencil, you haven’t resorted to billiard balls. The problem with injecting more jelly into the jelly is that, although it will distort the imaginary grid lines, it won’t create a pressure gradient, because the jelly you inserted is the same substance and will therefore take its fair share of the pressure. To create a genuine pressure gradient I think we need a boundary of substance. Intuitively, I think we agree, it seems abhorrent to resort to dropping a billiard ball in the jelly, but I think the incompressible bubble of nothingness is satisfactory because then the whole setup is literally “nothing more than space”.
.
I have no problems with holes. The eye of the storm is a hole. I think of the pilot wave as the particle, and other people think the particle is the hole in the middle. But my view on no-space is different to yours, so I think the best position to take is this: modelling photons and pair production and electrons and positrons ought to tell you something about all this stuff. Whether your no-space is solid space maybe doesn’t matter so much then.
.
Michelangelo sculpts his David out of marble + emptiness.
.
True. Something that really struck me was Einstein, in his 1920 Leyden Address, saying the contrast between space and matter will fade away. Something else was this in his 1930 Nottingham lecture: space “remains the sole medium of reality”. Another thing I like is the notion that matter is 99% empty space. Because I think that’s wrong by 1%!
.
But whatever, I think your blog is a work of outstanding brilliance and I’ve learnt more from reading it than from all the schooling I’ve had and books I’ve read, and I’m finding the discussion enthralling!
.
Thanks Jonathan. That makes it all worthwhile.
If matter is a standing light wave with 1/2 spin, then why is it only 511keV photons which can form matter? Why can’t say 1eV photons form a standing wave of 1/2 spin and create a “light electron” with a mass of 1eV, or am I missing something here?
If matter/electrons are basically standing light waves with a moebius twist (spin 1/2) then why is it that only 511keV light waves can accomplish this? Why don’t we have say 1eV “light electrons” being a mobius twisted 1eV photon (or any other energy different from 511keV) or am I missing something here?
Because E=hf applies to all photons, and the dimensionality of action h can be expressed as momentum x distance. I think this means that the amplitude of all photons is the same, and it’s a physical distance. Then if you want to trap a photon in a spin ½ double-loop “trivial knot” configuration, only one wavelength will do. It is a 2π multiple of that distance. See articles on particles, and read them in sequence.
John, thank you for this great article. Please, what you think about, may I call it a paradox – we possibly have no way to research ether (gin-clear elastic jelly like) in-situ, because we and our technology are only waves of stress of this jelly. Ridiculosly slight possibility I think of – is taking measures inside black holes (frozen star where it is possible ether is absent or in another state).
Thanks Tony. I don’t think there’s any possibility of taking measurements in a black hole because IMHO that’s a place where the aether, for want of a better word, is frozen solid. I think the speed of light, along with the speed of everything else at that location, is zero. If it wasn’t, the black hole wouldn’t be black.